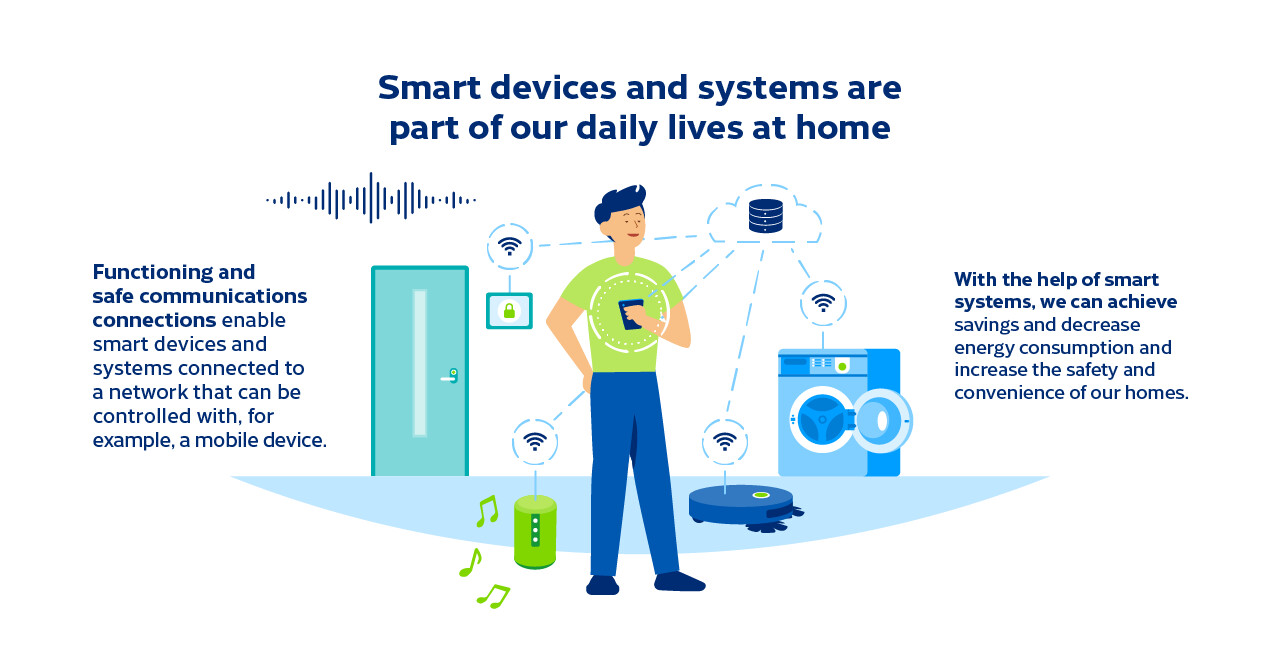
The number of smart devices in our homes and everyday lives is growing constantly. They come in all shapes and sizes, ranging from the familiar smartphones and wearable devices such as smartwatches to smart home appliances and all the way to devices used for purposes such as optimising building services equipment and electrical systems. All smart devices must be supported by reliable connections with good information security for the communication between different devices and users. In addition to this, smart homes need stable, high-performance broadband connections with good information security, through which the devices can connect to the outer world and a wide range of services.
At Traficom, our task is to promote the availability of high-speed and high-performance broadband connections in many different ways. We carry out frequency planning to ensure functionality and freedom from interference, and we are active in many different international forums where agreements are made on the use of radio frequencies needed by wireless connections.
The smart devices at our homes, like many other kinds of radio equipment used in our everyday lives, are mainly exempt from having a licence for radio broadcasting. In principle, our goal at Traficom is to always grant exemptions from the licence for radio equipment, if this is possible with regard to the frequencies and the interference-free use of devices. In this way, using radio equipment is smooth and easy. We also ensure that wireless devices sold in Finland that use radio frequencies, i.e. radio equipment, meet the requirements set for them.
In the fixed broadband network, we grant government support for the construction of optical fibre networks and provide a single information point to promote the shared construction of networks. For its part, the National Cyber Security Centre Finland of Traficom develops and monitors the safety and reliability of communications networks.
Finland has comprehensive broadband networks
Mobile networks play a central role in the different functions of society as well as the everyday lives of all of us. They also offer broadband connections for the needs of the smart devices at home. Measured on the international level, Finland has reliable and comprehensive mobile networks. The networks cover Finland from south to north and also enable the use of smart device and services when moving outside the home. Mobile networks cover nearly all households in Finland.
At homes and other indoor spaces, broadband connections are often based on mobile networks or fixed connections, such as optical fibre. Inside the home, the connections are often shared via a WLAN network from a router connected to a mobile network or a fixed broadband network to the various smart devices at home that need a connection.
As work is increasingly often hybrid work, where the share of location-independent and remote work has increased heavily, the importance of reliable broadband connections in everyday life has been emphasised further. Video conferences and the use of information on the workplace’s servers require connections that have sufficient performance and capacity for a smooth workflow.
At the moment, fifth-generation mobile network technology, also known as 5G, is being adopted in Finland. The performance of 5G technology is more efficient than the previous technology generations, enabling higher data transfer speeds, among other things. Operators are actively building 5G networks, and the networks currently cover already close to 90% of Finnish households. At the same time, the construction of fixed broadband progresses in different parts of Finland, and new areas are brought within the coverage of optical fibre, among other things.
Smart devices and systems as a part of the home
Traficom’s work in enabling the current and future use of radio frequencies is especially important, because the number of devices connected to the network wirelessly is growing constantly. The Internet of Things connects different kinds of sensors and cameras to the network. They help with collecting data from e.g. devices and their status, operating conditions and processes that make it possible to control various functions safely and effectively. In homes, things like smart building technology, lighting and the use of electricity can be implemented by taking advantage of devices and systems connected to the network that can be controlled with e.g. mobile devices.
Smart systems can help achieve savings, reduce energy consumption and improve the safety and comfort of living. During the first stage, we can control the different functions of home from touchscreens and surfaces as well as with voice control. Later, a smart home of the future can learn to adjust to us and our habits and be able to predict our needs in different situations. Well-working and safe telecommunications connections are at the centre of this development.
Market surveillance of smart devices prevents radio interference
Many smart devices operate wirelessly on radio frequencies. An agreement has been made on common minimum requirements for the wireless devices sold in the EU area, so that such devices that use frequencies would not interfere with each other, among other things. Before a wireless device can be sold within the EU, the device manufacturer must ensure that the device meets the requirements set for it and attach a CE marking to the device. The other actors in the delivery chain, such as importers and sellers, are also obliged to ensure that only devices that comply with the requirements are sold. Traficom monitors the compliance of radio equipment sold in the Finnish market, and the goal of the monitoring is to prevent radio interference. In the future, information security requirements will also apply to certain wireless devices sold within the EU; they will enter into force in the coming years.
Cyber security must be taken into account in all smart devices
Smart devices collect a lot of data on their users and send them further to the device manufacturers, and from there on to parties such as advertisers. It is important to pay attention to information security, so that the personal data of users are not collected without permission and breaking into user accounts is not possible, for example. Determining the level of information security of devices on the market may be difficult. Before making the decision to buy, it is good to find out from the seller and the manufacturer how information security has been implemented in the device, and how long does the manufacturer commit to updating the devices. One way of ensuring the safety of a smart device is to check if a Cybersecurity Label has been granted to the device. The label shows that the device meets the requirements set by the National Cyber Security Centre Finland of Traficom.
Traficom is actively involved in the international 6G development work
International work on developing the sixth-generation mobile network technology that aims to meet our future communication needs is currently in progress. The 6G technology that will be implemented around 2030 combines the physical, digital and biological worlds as well as billions of machines, devices, people, vehicles, robots and drones in a cloud via a network optimised by artificial intelligence. The cross-cutting themes of 6G development work include sustainable development, security and resilience, intelligence everywhere and enabling connections for all. Traficom actively participates in the international 6G development, and we closely influence the radio frequency work in the EU as well as internationally. Finland is one of the leading countries in communications technology, and for our part, we want to ensure that Finland also stays at the head of 6G development.
New technologies revolutionise smart home solutions
Technologies develop quickly, and new digital services are being created all the time. In the future, we will see many new digital services that we cannot even imagine yet. Computing and intelligence are an increasingly more important part of networks, and these functions are moving from the current centralised data centres and closer and closer to the users. In the future, data transfer may be based on a network of networks controlled by artificial intelligence that adapts seamlessly to the needs of the users and services at any given moment. This enables the development of new kinds of digital services, such as remote presence and the development of digital health and well-being solutions, as well as digital modelling of the physical world.
At the moment, it is believed that the potential breakthrough of the metaverse as well as platforms taking advantage of virtual and augmented reality will change how we consume digital content and services. It is thought that artificial intelligence will become an increasingly larger part of work and everyday life and help us with various tasks both at home and in the office. This development also poses challenges to the digital infrastructure and telecommunications networks. In fact, the future should also be kept in mind when designing the broadband solutions of your home, because the number of smart devices is growing and diversifying, and many new services require higher performance from telecommunications connections than before.
Read more about the requirements on wireless devices on Traficom’s website (External link)
You can also find the smart consumer’s checklist (in Finnish) at the address älyäostoksiin.fi (External link)
Read more about the Cybersecurity Label (External link)
Go back to the page “Radio frequencies now and in the future" (External link)